Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination
Types of Mutations
Problem 12a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionWhat is the phenotypic effect of inserting a Ds element into the maize C gene? How do Ds and Ac produce maize kernels that are mostly yellow with purple spots?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transposable Elements
Transposable elements, or 'jumping genes,' are DNA sequences that can change their position within the genome. In maize, the Dissociation (Ds) element is a type of transposable element that can disrupt gene function when inserted into a gene, such as the C gene, which is responsible for color in kernels. This insertion can lead to phenotypic changes, such as altered pigmentation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
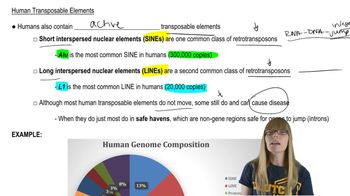
Human Transposable Elements
C Gene and Kernel Color
The C gene in maize is crucial for the production of anthocyanin pigments, which contribute to the color of the kernels. When the Ds element inserts into the C gene, it can disrupt its function, leading to a loss of pigment production. This results in kernels that may exhibit a yellow color due to the absence of anthocyanin, with purple spots appearing where the gene is still functional.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping Genes
Activator (Ac) and Dissociation (Ds) Interaction
The Ac (Activator) element is another transposable element that can promote the movement of Ds elements within the genome. When Ac is present, it can facilitate the excision of Ds from the C gene, potentially restoring its function in some cells. This interaction can create a mosaic pattern in the kernels, leading to a phenotype where most kernels are yellow, but some exhibit purple spots due to the reactivation of the C gene in specific areas.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Discovery

 9:49m
9:49mWatch next
Master Point Mutations with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning



