Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination
Types of Mutations
Problem 23b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionMutations in the CFTR gene result in cystic fibrosis in humans, a condition in which abnormal secretions are present in the lungs, pancreas, and sweat glands. The gene was mapped to a 500-kb region on chromosome 7 containing three candidate genes.
How would you prove that your chosen candidate is the CFTR gene?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
CFTR Gene Function
The CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) gene encodes a protein that functions as a channel for chloride ions across epithelial cell membranes. This regulation of ion transport is crucial for maintaining the balance of salt and water in various tissues, particularly in the lungs and pancreas. Mutations in the CFTR gene disrupt this function, leading to the thick, sticky mucus characteristic of cystic fibrosis.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Functional Genomics
Genetic Mapping
Genetic mapping involves identifying the location of genes on chromosomes and understanding their relationships to specific traits or diseases. In this context, mapping the CFTR gene to a 500-kb region on chromosome 7 helps narrow down potential candidate genes. Techniques such as linkage analysis and positional cloning are often used to establish these connections and identify genes associated with particular conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
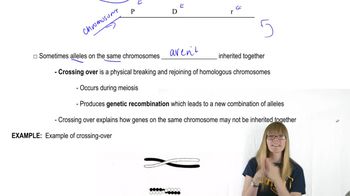
Mapping Overview
Mutation Analysis
Mutation analysis is a method used to identify specific changes in the DNA sequence of a gene that may lead to disease. To prove that a candidate gene is the CFTR gene, researchers can perform sequencing to detect known mutations associated with cystic fibrosis. Additionally, functional assays can be conducted to assess whether the candidate gene's protein product exhibits the characteristic ion transport activity of CFTR.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square Analysis

 9:49m
9:49mWatch next
Master Point Mutations with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning



