Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
10. Transcription
Transcription in Prokaryotes
Problem 29b
Textbook Question
The DNA sequence below gives the first 12 base pairs of the transcribed region of a gene, and the template and nontemplate strands of DNA are identified. The transcription start is the thymine nucleotide at the end of the sequence given. Use the diagram to answer the list of questions. Make a copy of the diagram before you begin answering the questions, or have one group member diagram the answers for bacteria and another group member diagram the answers for eukaryotes. Nontemplate strand ___________TTGCTACGGTCA___________ Template strand ___________AACGATGCCAGT___________ Assuming the sequence shown is part of a bacterial gene, what consensus sequence(s) would you expect to identify in the promoter?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the location of the promoter region in bacterial genes, which is typically upstream of the transcription start site.
Recall that in bacteria, common consensus sequences in the promoter region include the -10 (Pribnow box) and -35 regions.
The -10 consensus sequence is usually 'TATAAT', and the -35 consensus sequence is typically 'TTGACA'.
Determine the position of the transcription start site, which is the thymine nucleotide at the end of the given sequence.
Examine the sequence upstream of the transcription start site to identify any matches or similarities to the -10 and -35 consensus sequences.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Promoter Regions
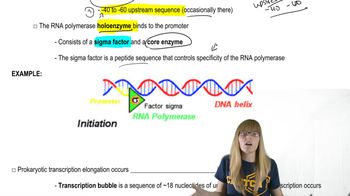
Promoter regions are specific sequences of DNA located upstream of a gene that serve as binding sites for RNA polymerase and transcription factors. In bacteria, common consensus sequences found in promoters include the -10 (Pribnow box) and -35 regions, which are crucial for the initiation of transcription. Understanding these sequences helps in predicting where transcription will begin and how efficiently a gene will be expressed.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Regions of X Chromosomes
Transcription in Bacteria
Transcription in bacteria is the process by which RNA is synthesized from a DNA template. It involves the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter region, followed by the unwinding of DNA and the synthesis of a complementary RNA strand. This process is essential for gene expression and is regulated by various factors, including the presence of specific consensus sequences in the promoter.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Eukaryotic Transcription
Consensus Sequences
Consensus sequences are short, recurring patterns in DNA that are recognized by proteins involved in transcription, such as RNA polymerase. These sequences represent the most common nucleotides found at specific positions in a set of related sequences and are critical for the binding of transcription machinery. Identifying these sequences in a promoter can provide insights into the regulation and efficiency of gene transcription.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Sequencing Overview

 1:14m
1:14mWatch next
Master Prokaryotic Transcription with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice