Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
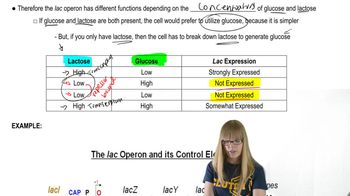
Lac Operon
Problem 20c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionA bacterial operon is responsible for the production of the biosynthetic enzymes needed to make the hypothetical amino acid tisophane (tis). The operon is regulated by a separate gene, R. The deletion of R causes the loss of enzyme synthesis. In the wild-type condition, when tis is present, no enzymes are made; in the absence of tis, the enzymes are made. Mutations in the operator gene (O⁻) result in repression regardless of the presence of tis. Is the operon under positive or negative control? Propose a model for (a) repression of the genes in the presence of tis in wild-type cells and (b) the mutations.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
38sPlay a video:
488
views
Was this helpful?
Related Videos
Related Practice