Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
11. Translation
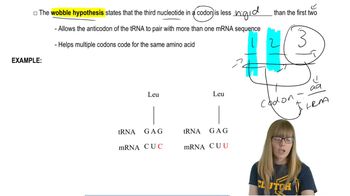
Translation
Problem 36a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionThe flow of genetic information from DNA to protein is mediated by messenger RNA. If you introduce short DNA strands (called antisense oligonucleotides) that are complementary to mRNAs, hydrogen bonding may occur and 'label' the DNA/RNA hybrid for ribonuclease-H degradation of the RNA. One study [Lloyd et al. (2001). Nucl. Acids Res. 29:3664–3673] compared the effect of different-length antisense oligonucleotides upon ribonuclease-H–mediated degradation of tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) mRNA. TNFα exhibits antitumor and pro-inflammatory activities. The following graph indicates the efficacy of various-sized antisense oligonucleotides in causing ribonuclease-H cleavage. What factors other than oligonucleotide length are likely to influence antisense efficacy in vivo?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
285
views
Was this helpful?