Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
6. Chromosomal Variation
Chromosomal Mutations: Aneuploidy
Problem 11a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionThe most common reason a physician might recommend that a woman have maternal serum screening and a karyotype analysis is concern that her fetus may have Down syndrome. Go to the OMIM website at www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim and look up Down syndrome (OMIM 190685).
List the main symptoms of Down syndrome.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Down Syndrome
Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. This condition leads to a range of developmental and physical challenges, including characteristic facial features, cognitive impairment, and an increased risk of certain health issues. Understanding the genetic basis of Down syndrome is crucial for recognizing its symptoms and implications.
Recommended video:
Guided course
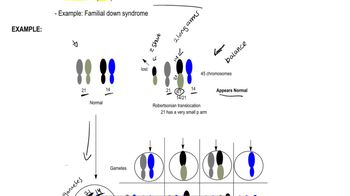
Robertsonian Translocations
Maternal Serum Screening
Maternal serum screening is a blood test performed during pregnancy to assess the risk of certain genetic conditions, including Down syndrome. It measures specific substances in the mother's blood that may indicate an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus. This screening is typically done in the first or second trimester and helps inform further diagnostic testing if necessary.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect
Karyotype Analysis
Karyotype analysis is a laboratory procedure that examines the number and structure of chromosomes in an individual's cells. This test can identify chromosomal abnormalities, such as the extra chromosome associated with Down syndrome. Karyotyping is often used as a follow-up to screening tests to confirm or rule out genetic disorders, providing critical information for prenatal care.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square Analysis
Related Videos
Related Practice




