Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis
Problem 1d
Textbook Question
Examine the following diagrams of cells from an organism with diploid number 2n=6, and identify what stage of M phase is represented.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the diploid number of the organism, which is 2n=6, meaning there are 6 chromosomes in total.
Understand that M phase, or mitosis, consists of several stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Examine the diagrams of the cells to determine the arrangement and appearance of the chromosomes.
Look for key characteristics of each stage: condensed chromosomes and spindle formation in prophase, alignment of chromosomes at the metaphase plate in metaphase, separation of sister chromatids in anaphase, and decondensation of chromosomes in telophase.
Match the observed characteristics in the diagrams to the descriptions of the stages to identify the specific stage of M phase represented.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
58sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
M Phase
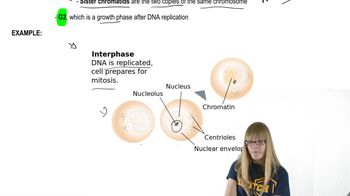
M Phase, or mitotic phase, is the stage of the cell cycle where cell division occurs. It includes both mitosis, the process of nuclear division, and cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm. Understanding M Phase is crucial for identifying the specific stage represented in the diagrams, as it encompasses several distinct phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Cancer Causes
Diploid Number
The diploid number (2n) refers to the total number of chromosomes in a somatic cell, where chromosomes exist in pairs. In this case, 2n=6 indicates that the organism has six chromosomes, or three pairs. Recognizing the diploid number helps in understanding the genetic makeup of the organism and the implications for chromosome behavior during M Phase.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Diploid Genetics
Chromosome Structure During M Phase
During M Phase, chromosomes undergo significant structural changes, becoming highly condensed and visible under a microscope. Each chromosome consists of two sister chromatids joined at the centromere. Identifying the arrangement and number of chromatids in the diagrams is essential for determining the specific stage of M Phase, as the appearance of chromosomes varies between prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromosome Structure
Related Videos
Related Practice