Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Development of Animal Gametes
Problem 24
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIf one follows 50 primary oocytes in an animal through their various stages of oogenesis, how many secondary oocytes would be formed? How many first polar bodies would be formed? How many ootids would be formed? If one follows 50 primary spermatocytes in an animal through their various stages of spermatogenesis, how many secondary spermatocytes would be formed? How many spermatids would be formed?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oogenesis
Oogenesis is the process of female gamete (egg) formation in animals. It begins with primary oocytes, which undergo meiosis to produce secondary oocytes and polar bodies. Each primary oocyte typically yields one functional secondary oocyte and one polar body, which may not contribute to fertilization. Understanding this process is crucial for determining the number of secondary oocytes and polar bodies formed from a given number of primary oocytes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Gamete Development
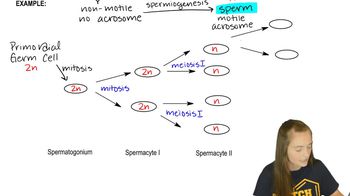
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process of male gamete (sperm) formation, occurring in the testes. It starts with primary spermatocytes that undergo meiosis to produce secondary spermatocytes, which then further divide to form spermatids. Each primary spermatocyte results in four spermatids after two meiotic divisions. This concept is essential for calculating the number of secondary spermatocytes and spermatids produced from a specified number of primary spermatocytes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Gamete Development
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse gametes. It consists of two sequential divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II. In oogenesis and spermatogenesis, meiosis is responsible for the formation of secondary oocytes and spermatocytes, respectively, and ultimately leads to the production of mature gametes. A solid understanding of meiosis is vital for answering questions about gamete formation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Meiosis Overview

 21:21m
21:21mWatch next
Master Gamete Development with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

