Textbook Question
Write the Lewis structure for each molecule (octet rule not followed). b. NO2
825
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

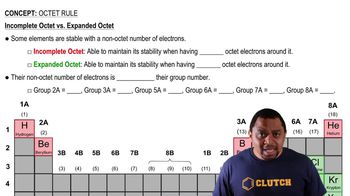

Write the Lewis structure for each molecule (octet rule not followed). b. NO2
Write the Lewis structure for each molecule (octet rule not followed). a. BBr3 b. NO c. ClO2
Write Lewis structures for each molecule or ion. Use expanded octets as necessary. a. PF5
Order these compounds in order of increasing carbon–carbon bond strength: HCCH, H2CCH2, H3CCH3.
Order these compounds in order of decreasing carbon–carbon bond length: HCCH, H2CCH2, H3CCH3.
Which of the two compounds, H2NNH2 and HNNH, has the strongest nitrogen-nitrogen bond, and which has the shorter nitrogen-nitrogen bond.