Use Lewis symbols to determine the formula for the compound that forms between each pair of elements. a. Mg and S b. Sr and Br c. K and Se d. Al and S
The lattice energy of CsF is -744 kJ/mol, whereas that of BaO is -3029 kJ/mol. Explain this large difference in lattice energy.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Lattice Energy

Ionic Charge

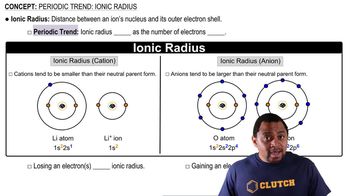
Ionic Radius
Use Lewis symbols to determine the formula for the compound that forms between each pair of elements. a. Sr and P b. Ba and S c. Sr and Se d. Rb and I
Rubidium iodide has a lattice energy of -617 kJ/mol, while potassium bromide has a lattice energy of -671 kJ/mol. Why is the lattice energy of potassium bromide more exothermic than the lattice energy of rubidium iodide?
Arrange these compounds in order of increasing magnitude of lattice energy: CaO, NaBr, CsI, BaS.
Use the Born–Haber cycle and data from Appendix IIB, Chapter 9 and this chapter to calculate the lattice energy of LiBr. (ΔHsub for lithium is 138 kJ>mol.)
Use the Born–Haber cycle and data from Appendix IIB and Table 10.3 to calculate the lattice energy of MgO. (ΔHsub for magnesium is 137 kJ/mol; IE1 and IE2 for magnesium are 738 kJ/mol and 1450 kJ/mol, respectively; EA1 and EA2 for O are −141 kJ/mol and 744 kJ/mol, respectively.)
