The reaction of Fe2O3(s) with Al(s) to form Al2O3(s) and Fe(s) is called the thermite reaction and is highly exothermic. What role does lattice energy play in the exothermicity of the reaction?
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model
Chapter 10, Problem 104c
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. c. CH3COCH3
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the central atoms in the compound. In CH$_3$COCH$_3$, the central atoms are the carbon atoms.
Determine the connectivity of the atoms. The structure is CH$_3$-C(=O)-CH$_3$, where the middle carbon is double-bonded to an oxygen.
Draw the carbon skeleton. Connect the carbon atoms in a chain: C-C-C.
Add the oxygen atom. Attach the oxygen to the middle carbon with a double bond: C(=O).
Complete the structure by adding hydrogen atoms. Each terminal carbon (CH$_3$) is bonded to three hydrogen atoms.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
59sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. They use dots to represent electrons and lines to represent bonds between atoms. Understanding how to draw Lewis structures is essential for visualizing molecular geometry and predicting reactivity.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
Condensed Structural Formula
A condensed structural formula provides a shorthand way of representing the structure of a molecule, showing how atoms are connected without depicting all the bonds explicitly. For example, in CH3COCH3, the formula indicates that there are two methyl groups (CH3) attached to a carbonyl group (C=O), which is crucial for understanding the molecular structure before drawing the Lewis structure.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Condensed Formula
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In the case of CH3COCH3, the carbonyl group (C=O) is a functional group that defines the compound as a ketone, influencing its chemical behavior and properties. Recognizing functional groups is vital for predicting reactivity and understanding organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
Guided course
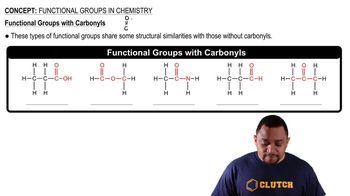
Carbonyl Functional Groups
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1197
views
Textbook Question
NaCl has a lattice energy of -787 kJ/mol. Consider a hypothetical salt XY. X3+ has the same radius of Na+ and Y3- has the same radius as Cl-. Estimate the lattice energy of XY.
1191
views
Textbook Question
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. b. CH3OCH3
558
views
Textbook Question
Draw the Lewis structure for each organic compound from its condensed structural formula. e. CH3CHO
879
views
Textbook Question
Use Lewis structures to explain why Br3- and I3- are stable, while F3- is not.
825
views
Textbook Question
Draw the Lewis structure for urea, H2NCONH2, one of the compounds responsible for the smell of urine. (The central carbon atom is bonded to both nitrogen atoms and to the oxygen atom.) Does urea contain polar bonds? Which bond in urea is most polar?
1666
views
