Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Orbital Diagrams
Orbital diagrams visually represent the distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals. Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins, and the diagram helps illustrate how electrons fill these orbitals according to the Aufbau principle, Hund's rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle. Understanding how to construct these diagrams is essential for determining the electron configuration of ions.
Recommended video:
Electron Orbital Diagrams
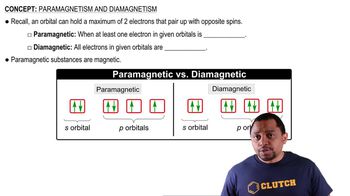
Diamagnetism vs. Paramagnetism
Diamagnetism and paramagnetism are two types of magnetic behavior in materials. Diamagnetic substances have all their electrons paired, resulting in no net magnetic moment and weak repulsion from magnetic fields. In contrast, paramagnetic substances have unpaired electrons, leading to a net magnetic moment and attraction to magnetic fields. Identifying whether an ion is diamagnetic or paramagnetic is crucial for understanding its chemical properties.
Recommended video:
Paramagnetism vs Diamagnetism
Electron Configuration of Ions
The electron configuration of ions is derived from the electron configuration of the neutral atom, adjusted for the loss or gain of electrons. For cations, electrons are removed from the outermost orbitals first, which can affect the overall electron arrangement. Knowing how to write the electron configuration for ions like V<sup>5+</sup>, Cr<sup>3+</sup>, Ni<sup>2+</sup>, and Fe<sup>3+</sup> is vital for constructing their orbital diagrams and determining their magnetic properties.
Recommended video:
Anion Electron Configuration
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance