The iodide ion is a dietary mineral essential to good nutrition. In countries where potassium iodide is added to salt, iodine deficiency (or goiter) has been almost completely eliminated. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for iodine is 150 mg/day. How much potassium iodide (76.45% I) should you consume if you want to meet the RDA?
Ch.3 - Molecules and Compounds
Chapter 3, Problem 88b
Write a ratio showing the relationship between the molar amounts of each element for each compound. (See Appendix IIA for color codes.) (b)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the elements in the molecular models using the color code provided: White for Hydrogen (H), Green for Nitrogen (N), and Pink for Carbon (C).
Count the number of each type of atom in one of the molecular models. For example, count the number of white (H), green (N), and pink (C) spheres in one molecule.
Write down the molar amounts of each element in the form of a ratio. For instance, if a molecule has 2 H, 1 N, and 1 C, the ratio would be H:N:C = 2:1:1.
Repeat the counting process for each different molecular model shown in the image to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Compare the ratios obtained for each molecular model to understand the relationship between the molar amounts of each element in the compounds.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molar Ratios
Molar ratios express the relationship between the amounts of different substances in a chemical reaction or compound. They are derived from the coefficients in a balanced chemical equation and indicate how many moles of one substance react with or produce moles of another. Understanding molar ratios is essential for stoichiometric calculations in chemistry.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Neutron-Proton Ratio
Chemical Formulas
Chemical formulas represent the composition of a compound, showing the types and numbers of atoms present. For example, in the formula C2H6, there are two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. Analyzing chemical formulas allows students to determine the molar amounts of each element in a compound, which is crucial for calculating ratios.
Recommended video:
Guided course
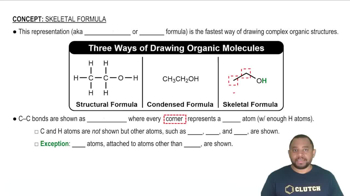
Skeletal Formula
Molecular Models
Molecular models visually represent the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. They help in understanding the spatial relationships and bonding between different atoms. The image provided illustrates molecular models of compounds containing hydrogen (H), nitrogen (N), and carbon (C), which aids in visualizing how these elements combine and their respective ratios in the compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bohr Model of the Atom
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1365
views
Textbook Question
The American Dental Association recommends that an adult female should consume 3.0 mg of fluoride (F-) per day to prevent tooth decay. If the fluoride is consumed in the form of sodium fluoride (45.24% F), what amount of sodium fluoride contains the recommended amount of fluoride?
1422
views
Textbook Question
Write a ratio showing the relationship between the molar amounts of each element for each compound. (See Appendix IIA for color codes.) (a)
576
views
Textbook Question
Determine the number of moles of hydrogen atoms in each sample. a. 0.0885 mol C4H10 b. 1.3 mol CH4
3429
views
Textbook Question
Determine the number of moles of hydrogen atoms in each sample. c. 2.4 mol C6H12
1527
views
Textbook Question
Determine the number of moles of hydrogen atoms in each sample. d. 1.87 mol C8H18
711
views
