Textbook Question
Determine whether or not each metal, if coated onto iron, would prevent the corrosion of iron. a. Zn
299
views
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


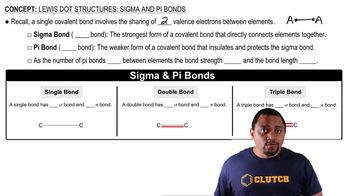
Determine whether or not each metal, if coated onto iron, would prevent the corrosion of iron. a. Zn
Determine whether or not each metal, if coated onto iron, would prevent the corrosion of iron. b. Sn
Determine whether or not each metal, if coated onto iron, would prevent the corrosion of iron. c. Mn
Determine whether or not each metal, if coated onto iron, would prevent the corrosion of iron. b. Cr
Determine whether or not each metal, if coated onto iron, would prevent the corrosion of iron. c. Cu
Consider the electrolytic cell: b. Indicate the direction of electron flow.