A formic acid solution has a pH of 3.25. Which of these substances will raise the pH of the solution upon addition? Explain your answer. a. HCl b. NaBr c. NaCHO2 d. KCl
Ch.18 - Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium
Chapter 18, Problem 31
Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.20 M benzoic acid solution in pure water and in a solution containing 0.25 M sodium benzoate. Why does the percent ionization differ significantly in the two solutions?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1: Write the chemical equation for the ionization of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) in water: C6H5COOH (aq) ⇌ C6H5COO⁻ (aq) + H⁺ (aq).
insert step 2: Use the expression for the acid dissociation constant (Ka) for benzoic acid: Ka = [C6H5COO⁻][H⁺] / [C6H5COOH].
insert step 3: For the pure water solution, set up an ICE table (Initial, Change, Equilibrium) to find the equilibrium concentrations of the species involved. Assume initial concentration of benzoic acid is 0.20 M and initial concentrations of C6H5COO⁻ and H⁺ are 0.
insert step 4: For the solution containing sodium benzoate, recognize that sodium benzoate is a salt that provides a common ion (C6H5COO⁻). Use the common ion effect to adjust the ICE table, starting with an initial concentration of 0.25 M for C6H5COO⁻.
insert step 5: Calculate the percent ionization for both scenarios using the formula: Percent Ionization = ([H⁺] / Initial [C6H5COOH]) * 100%. Compare the results to understand the effect of the common ion on ionization.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
6mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionization of Weak Acids
Weak acids, like benzoic acid, do not completely dissociate in solution. Instead, they establish an equilibrium between the undissociated acid and its ions. The degree of ionization is influenced by the acid's strength, which is quantified by its acid dissociation constant (Ka). Understanding this equilibrium is crucial for calculating percent ionization.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Calculating Percent Ionization of Weak Acids
Percent Ionization
Percent ionization is a measure of the extent to which an acid dissociates in solution, expressed as the ratio of the concentration of ionized acid to the initial concentration, multiplied by 100. It provides insight into the strength of the acid in different environments, helping to compare how factors like concentration and the presence of other solutes affect ionization.
Recommended video:
Guided course
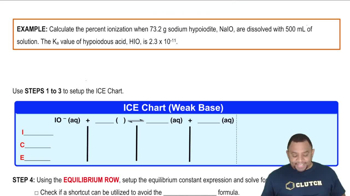
Percent Ionization Example
Common Ion Effect
The common ion effect occurs when a salt containing an ion in common with a weak acid is added to the solution, shifting the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier's principle. In the case of benzoic acid and sodium benzoate, the presence of benzoate ions from sodium benzoate suppresses the ionization of benzoic acid, leading to a lower percent ionization in the mixed solution compared to pure water.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Common Ion Effect
Related Practice
Textbook Question
2806
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. a. a solution that is 0.25 M in NH3 and 0.18 M in NH4Cl
Textbook Question
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. b solution that is 0.15 M in HCHO2 and 0.25 M in NaCHO2
Textbook Question
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. a. 0.15 M HF
1231
views
Textbook Question
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. b. 0.15 M NaF
508
views
Textbook Question
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. c. a mixture that is 0.15 M in HF and 0.15 M in NaF
1765
views
