Textbook Question
Determine the [H3O+] and pH of a 0.100 M solution of formic acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
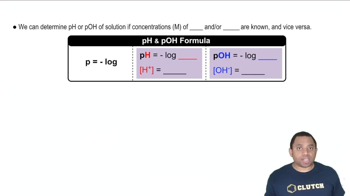


Determine the [H3O+] and pH of a 0.100 M solution of formic acid.
Determine the pH of an HNO2 solution of each concentration. In which cases can you not make the simplifying assumption that x is small? a. 0.500 M b. 0.100 M c. 0.0100 M
Determine the pH of an HF solution of each concentration. In which cases can you not make the simplifying assumption that x is small? (Ka for HF is 6.8×10–4.) a. 0.250 M b. 0.0500 M c. 0.0250 M
Determine the percent ionization of a 0.100 M HCN solution.
Determine the percent ionization of a 0.250 M solution of benzoic acid.
Calculate the percent ionization of a formic acid solution having the given concentration. a. 1.00 M