Molecular Solids
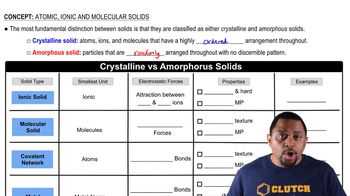
Molecular solids are composed of molecules held together by intermolecular forces such as van der Waals forces, dipole-dipole interactions, or hydrogen bonds. These solids typically have low melting and boiling points compared to ionic or atomic solids. Examples include ice (solid water) and sugar. The properties of molecular solids are largely influenced by the types of molecules and the strength of the intermolecular forces present.
Recommended video:
Crystalline vs Amorphous Solids
Ionic Solids
Ionic solids consist of positively and negatively charged ions held together by strong electrostatic forces known as ionic bonds. These solids generally have high melting and boiling points due to the strength of the ionic interactions. Common examples include sodium chloride (table salt) and magnesium oxide. Ionic solids are typically brittle and can conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water, as the ions are free to move.
Recommended video:
Ionic Solid Identification Example
Atomic Solids
Atomic solids are composed of atoms held together by covalent bonds, metallic bonds, or van der Waals forces, depending on the type of atomic solid. They can be further categorized into covalent network solids, like diamond, which have very high melting points, and metallic solids, which conduct electricity and heat well. The arrangement and bonding of atoms in these solids determine their physical properties, such as hardness and conductivity.
Recommended video:
Crystalline vs Amorphous Solids
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance