Write the Lewis symbols for the ions in each ionic compound. b. Li2S
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model
Chapter 10, Problem 42
Use Lewis symbols to determine the formula for the compound that forms between each pair of elements. a. Ca and N b. Mg and I c. Ca and S d. Cs and F
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the valence electrons for each element using the periodic table.
Use Lewis symbols to represent the valence electrons for each element.
Determine how many electrons each element needs to gain or lose to achieve a full outer shell (octet rule).
Pair the elements such that the total number of electrons lost by the metal equals the total number of electrons gained by the non-metal.
Write the chemical formula by balancing the charges to ensure the compound is neutral.

Verified Solution
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Symbols
Lewis symbols represent the valence electrons of an atom as dots around the element's symbol. This visual representation helps in understanding how atoms bond with each other by either sharing or transferring electrons. For example, the Lewis symbol for calcium (Ca) shows two dots, indicating its two valence electrons, which are crucial for forming ionic or covalent bonds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lewis Dot Symbols
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding occurs when one atom donates electrons to another, resulting in the formation of charged ions. This typically happens between metals, which lose electrons, and nonmetals, which gain electrons. For instance, in the case of calcium (Ca) and nitrogen (N), calcium loses two electrons to form Ca²⁺, while nitrogen gains three electrons to form N³⁻, leading to the compound Ca₃N₂.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chemical Bonds
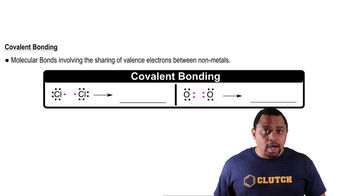
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms, usually between nonmetals. This type of bond is characterized by the formation of molecules where the shared electrons allow each atom to achieve a stable electron configuration. For example, when magnesium (Mg) bonds with iodine (I), they share electrons to form MgI₂, illustrating the concept of covalent bonding in molecular compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Chemical Bonds
Related Practice
Textbook Question
756
views
Textbook Question
Write the Lewis symbols for the ions in each ionic compound. c. CaI2
750
views
Textbook Question
Use Lewis symbols to determine the formula for the compound that forms between each pair of elements. a. Sr and Se b. Ba and Cl c. Na and S d. Al and O
992
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
Rubidium iodide has a lattice energy of -617 kJ/mol, while potassium bromide has a lattice energy of -671 kJ/mol. Why is the lattice energy of potassium bromide more exothermic than the lattice energy of rubidium iodide?
1490
views
Textbook Question
The lattice energy of CsF is -744 kJ/mol, whereas that of BaO is -3029 kJ/mol. Explain this large difference in lattice energy.
2194
views
Textbook Question
Use the Born–Haber cycle and data from Appendix IIB, Chapter 9 and this chapter to calculate the lattice energy of KCl. (ΔHsub for potassium is 89.0 kJ>mol.)
