Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Disubstituted Benzene
Disubstituted benzene refers to a benzene ring that has two substituent groups attached to it. The positions of these substituents can significantly affect the chemical properties and reactivity of the compound. The naming of disubstituted benzenes follows specific rules based on the relative positions of the substituents, which can be ortho (1,2-), meta (1,3-), or para (1,4-).
Recommended video:
Nomenclature of Aromatic Compounds
The nomenclature of aromatic compounds, particularly disubstituted benzenes, is governed by the IUPAC naming conventions. The base name is derived from benzene, and the substituents are named as prefixes. The positions of the substituents are indicated by numbers or by using the terms ortho, meta, and para, which help in identifying the structure of the compound clearly.
Recommended video:
Substituent Effects
Substituent effects refer to how different groups attached to a benzene ring influence its reactivity and stability. Some substituents are electron-donating (activating) and increase the electron density of the ring, while others are electron-withdrawing (deactivating) and decrease it. Understanding these effects is crucial for predicting the outcomes of electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions and for determining the preferred positions for new substituents.
Recommended video:
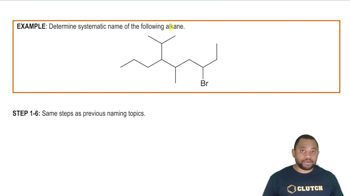
Naming Other Substituents Example
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance