Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alcohol Functional Group
Alcohols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached to a carbon atom. The general formula for alcohols is R-OH, where R represents a hydrocarbon chain. Understanding the functional group is essential for identifying the properties and reactivity of alcohols.
Recommended video:
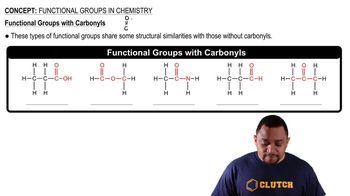
Carbonyl Functional Groups
IUPAC Nomenclature
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature provides a systematic way to name chemical compounds. For alcohols, the name includes the longest carbon chain containing the hydroxyl group, with the suffix '-ol' indicating the presence of the alcohol functional group. In '3-ethyl-1-hexanol', 'hexanol' indicates a six-carbon chain with an alcohol, while '3-ethyl' specifies a two-carbon ethyl group attached to the third carbon.
Recommended video:
Structural Representation
Drawing the structure of a compound involves representing its atoms and the bonds between them. For alcohols, this includes showing the carbon backbone, the hydroxyl group, and any substituents. In the case of 3-ethyl-1-hexanol, the structure must depict a six-carbon chain with an ethyl group branching off the third carbon, ensuring clarity in the molecular arrangement.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance