A substance has a band gap of 6.9 eV at 273 K. Is this substance best classified as an insulator, a semiconductor, or a metal?
Teflon is an addition polymer formed from the monomer shown here. Draw the structure of the polymer.


Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Addition Polymerization
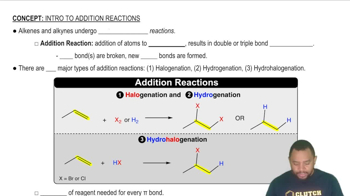
Monomer Structure

Polymer Structure Representation

Indicate if each solid forms an n-type or a p-type semiconductor.
a. silicon doped with gallium
b. germanium doped with antimony
Does a photon of red light with a frequency of 4.29⨉1014 Hz have sufficient energy to promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band in a sample of silicon (the band gap in silicon is 1.11 eV)?
Saran, the polymer used to make saran wrap, is an addition polymer formed from two monomers—vinylidene chloride and vinyl chloride. Draw the structure of the polymer. (Hint: The monomers alternate.)
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is an addition polymer with the struc- ture shown here. Draw the structure of the monomer.
Copper iodide crystallizes in the zinc blende structure. The sep- aration between nearest neighbor cations and anions is approximately 311 pm, and the melting point is 606 °C. Potassium chloride, by contrast, crystallizes in the rock salt structure. Even though the separation between nearest-neighbor cations and anions is greater (319 pm), the melting point of potassium chlo- ride is higher (776 °C). Explain.
