Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ideal Gas Law
The Ideal Gas Law is a fundamental equation in chemistry that relates the pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), and number of moles (n) of a gas. It is expressed as PV = nRT, where R is the ideal gas constant. This law helps predict how changing one of these variables affects the others, making it essential for understanding gas behavior under different conditions.
Recommended video:
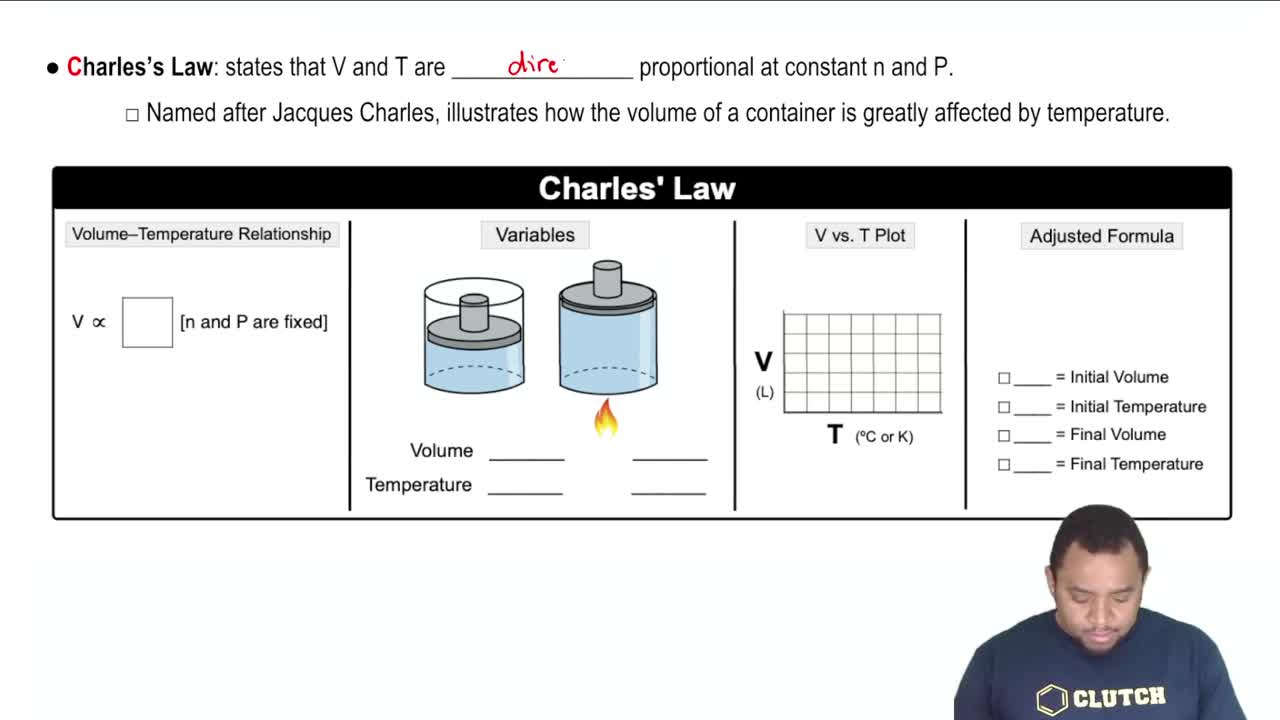
Charles's Law
Charles's Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is held constant. This means that if the temperature increases, the volume must also increase, and vice versa. In the context of the question, reducing the volume while increasing the temperature will significantly affect the pressure of the gas.
Recommended video:
Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law describes the inverse relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. According to this law, if the volume of a gas decreases, the pressure increases, provided the temperature remains constant. This principle is crucial for understanding how the pressure of the gas sample will change when its volume is halved.
Recommended video: