Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molarity (M)
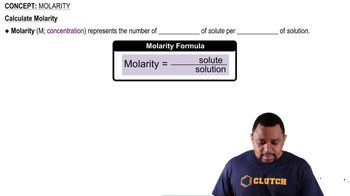
Molarity is a measure of concentration defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. In this case, a 1.35 M NaCl solution means there are 1.35 moles of sodium chloride dissolved in one liter of the solution. Understanding molarity is essential for calculating the mass of solute in a given volume of solution.
Recommended video:
Density
Density is the mass of a substance per unit volume, typically expressed in grams per milliliter (g/mL) for liquids. The density of the NaCl solution is given as 1.05 g/mL, which allows us to convert the volume of the solution into mass. This conversion is crucial for determining the total mass of the solution needed to find the percent by mass of sodium chloride.
Recommended video:
Percent by Mass
Percent by mass is a way to express the concentration of a component in a mixture, calculated as the mass of the solute divided by the total mass of the solution, multiplied by 100. To find the percent by mass of sodium chloride in the solution, we need to determine the mass of NaCl and the total mass of the solution, then apply this formula. This concept is fundamental for understanding the composition of solutions.
Recommended video: