A 67.2 g sample of a gold and palladium alloy contains 2.49×1023 atoms. What is the composition (by mass) of the alloy?
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets limits on healthful levels of air pollutants. The maximum level that the EPA considers safe for lead air pollution is 1.5 µg/m3. If your lungs were filled with air containing this level of lead, how many lead atoms would be in your lungs? (Assume a total lung volume of 5.50 L.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
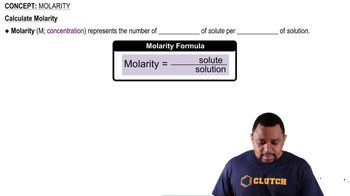
Key Concepts
Molarity and Concentration
Volume Conversion

Avogadro's Number

Naturally occurring chlorine is composed of two isotopes: 75.76% Cl-35 (mass 34.9688 amu) and 24.24% Cl-37 (mass 36.9659 amu). Naturally occurring oxygen is composed of three isotopes: 99.757% O-16 (mass 15.9949 amu), 0.038% O-17 (mass 16.9991 amu), and 0.205% O-18 (mass 17.9991 amu). The compound dichlorine monoxide is composed of two chlorine atoms and one oxygen atom bonded together to form the Cl2O molecule. How many Cl2O molecules of different masses naturally exist? Give the masses of the three most abundant Cl2O molecules.
Silver is composed of two naturally occurring isotopes: Ag-107 (51.839%) and Ag-109. The ratio of the masses of the two isotopes is 1.0187. What is the mass of Ag-107?
Pure gold is usually too soft for jewelry, so it is often alloyed with other metals. How many gold atoms are in an 0.255-ounce, 18 K gold bracelet? (18 K gold is 75% gold by mass.)
A volatile liquid (one that easily evaporates) is put into a jar and the jar is then sealed. Does the mass of the sealed jar and its contents change upon the vaporization of the liquid?
Let a triangle represent atoms of element A and a circle represent atoms of element B. b. Draw an atomic view of the compound AB in a liquid state (molecules close together).
