Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Standard Molar Entropy
Standard molar entropy (S°) is a measure of the amount of disorder or randomness in a system at standard conditions (1 bar, 25°C). It reflects the number of accessible microstates for a substance, with higher values indicating greater disorder. Entropy increases with molecular complexity, molecular weight, and the number of atoms in a molecule.
Recommended video:
Phase of Matter
The phase of matter significantly influences entropy. Gases generally have higher entropies than liquids and solids due to their greater freedom of movement and higher number of microstates. Among gases, larger and more complex molecules tend to have higher entropies than smaller, simpler ones, as they can occupy more spatial configurations.
Recommended video:
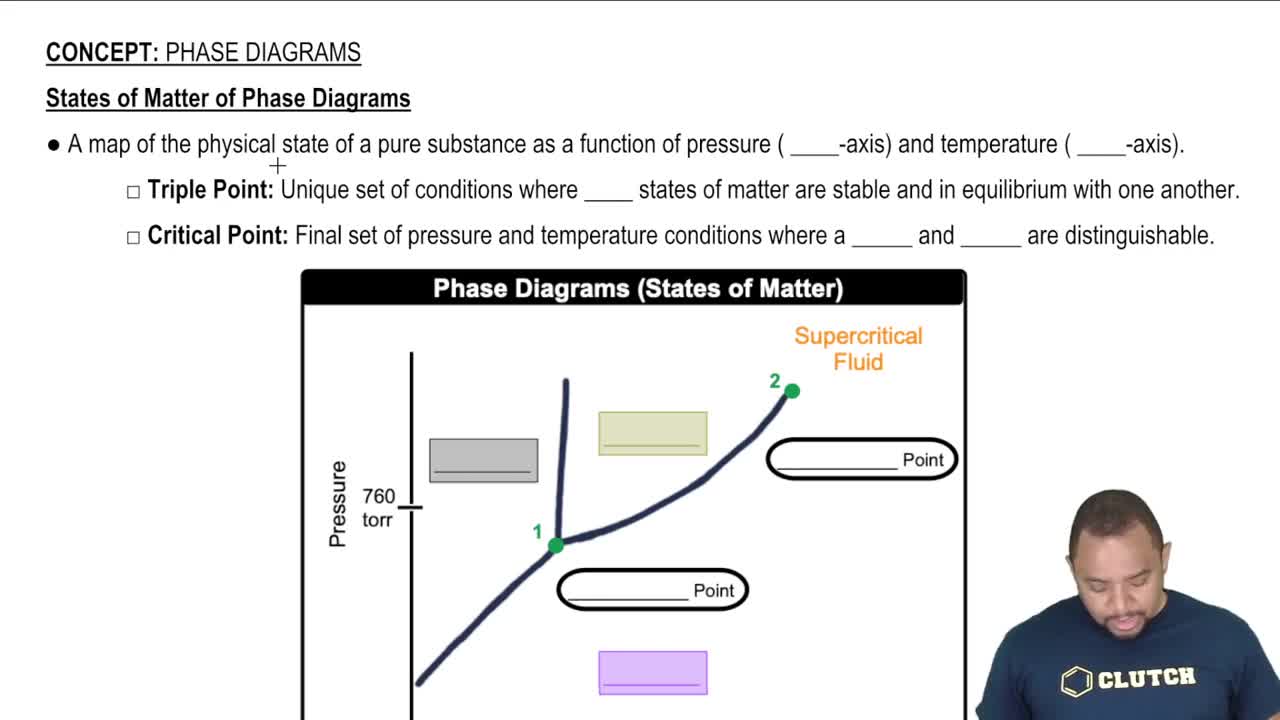
States of Matter of Phase Diagrams
Molecular Structure and Complexity
The molecular structure and complexity of a substance affect its entropy. Larger molecules with more atoms and functional groups can vibrate and rotate in more ways, leading to higher entropy. For example, comparing NH3 and CH3CH2OH, the latter has a more complex structure and thus a higher standard molar entropy due to increased molecular interactions and configurations.
Recommended video: