Determine if each anion acts as a weak base in solution. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. a. Br– b. ClO– c. CN– d. Cl–
Ch.16 - Acids and Bases
Chapter 16, Problem 97
Determine the [OH–] and pH of a solution that is 0.140 M in F–.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the relevant chemical equilibrium: The fluoride ion (F-) is the conjugate base of the weak acid HF, and it can undergo hydrolysis in water: \[ \text{F}^- + \text{H}_2\text{O} \rightleftharpoons \text{HF} + \text{OH}^- \].
Write the expression for the equilibrium constant (K_b) for the reaction: \[ K_b = \frac{[\text{HF}][\text{OH}^-]}{[\text{F}^-]} \].
Determine the value of K_b: Use the relationship \( K_w = K_a \times K_b \), where \( K_w = 1.0 \times 10^{-14} \) and \( K_a \) for HF is known from tables.
Set up an ICE table (Initial, Change, Equilibrium) to find the equilibrium concentrations of the species involved, assuming initial concentration of F- is 0.140 M and initial concentrations of HF and OH- are 0.
Solve for \([\text{OH}^-]\) using the K_b expression and the values from the ICE table, then calculate the pH using the relation \( \text{pH} = 14 - \text{pOH} \), where \( \text{pOH} = -\log[\text{OH}^-] \).

Verified Solution
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid-Base Chemistry
Acid-base chemistry involves the study of the transfer of protons (H+) between species. In this context, fluoride ion (F-) acts as a weak base, which can accept protons from water, leading to the formation of hydroxide ions (OH-) and hydrofluoric acid (HF). Understanding this equilibrium is crucial for determining the concentration of OH- and the resulting pH of the solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Arrhenius Acids and Bases
Equilibrium Constant (Kb)
The equilibrium constant for the base dissociation reaction (Kb) quantifies the strength of a weak base. For fluoride, the reaction can be represented as F- + H2O ⇌ HF + OH-. The Kb value allows us to calculate the concentration of OH- produced in the solution, which is essential for determining the pH. Knowing Kb is vital for solving the problem accurately.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Equilibrium Constant K
pH and pOH Relationship
The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, while pOH measures the concentration of hydroxide ions. They are related by the equation pH + pOH = 14 at 25°C. Once the concentration of OH- is determined, pOH can be calculated, and subsequently, pH can be derived. This relationship is fundamental for interpreting the results of the calculations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
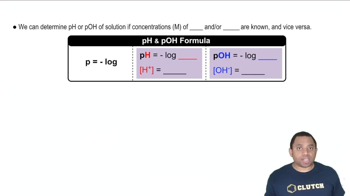
pH and pOH Calculations
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1124
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether each anion is basic or neutral. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. a. C7H5O2– b. I– d. F–
Textbook Question
Determine whether each anion is basic or neutral. For those anions that are basic, write an equation that shows how the anion acts as a base. c. NO3–
1243
views
Open Question
Determine the [OH-] and pH of a solution that is 0.250 M in HCO3⁻.
Textbook Question
Determine whether each cation is acidic or pH-neutral. For those cations that are acidic, write an equation that shows how the cation acts as an acid. a. NH4+
657
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether each cation is acidic or pH-neutral. For those cations that are acidic, write an equation that shows how the cation acts as an acid. b. Na+
382
views
