Based on these molecular views, determine whether each pictured acid is weak or strong.
Carbon dioxide dissolves in water according to the equations:
CO2(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq)
H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCO3–(aq) + H3O+(aq)
Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have increased about 20% over the last century. Given that Earth's oceans are exposed to atmospheric carbon dioxide, what effect might the increased CO2 be having on the pH of the world's oceans? What effect might this change be having on the limestone structures (primarily CaCO3) of coral reefs and marine shells?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
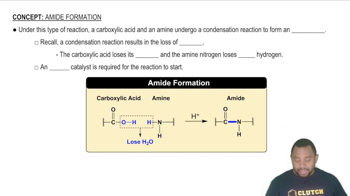
Key Concepts
Carbonic Acid Formation
Ocean Acidification

Impact on Calcium Carbonate Structures

Based on these molecular views, determine whether each pictured acid is weak or strong.
The binding of oxygen by hemoglobin in the blood involves the equilibrium reaction: HbH+(aq) + O2(aq) ⇌ HbO2(aq) + H+(aq) In this equation, Hb is hemoglobin. The pH of normal human blood is highly controlled within a range of 7.35 to 7.45. Given the above equilibrium, why is this important? What would happen to the oxygen-carrying capacity of hemoglobin if blood became too acidic (a dangerous condition known as acidosis)?
People often take milk of magnesia to reduce the discomfort associated with acid stomach or heartburn. The recommended dose is 1 teaspoon, which contains 4.00×102 mg of Mg(OH)2. What volume of an HCl solution with a pH of 1.3 can be neutralized by one dose of milk of magnesia? If the stomach contains 2.00×102 mL of pH 1.3 solution, is all the acid neutralized? If not, what fraction is neutralized?
Lakes that have been acidified by acid rain can be neutralized by liming, the addition of limestone (CaCO3). How much limestone (in kg) is required to completely neutralize a 4.3 billion liter lake with a pH of 5.5?
