Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acidity and pH
Acidity refers to the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution, which determines its pH level. A lower pH indicates a more acidic solution, while a higher pH indicates a more basic solution. Understanding the pH scale is essential for comparing the acidity of different solutions.
Recommended video:
pH of Strong Acids and Bases
Salt Hydrolysis
Salt hydrolysis occurs when a salt dissolves in water and reacts with water to produce an acidic or basic solution. For example, ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) can release H+ ions, making the solution acidic, while sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) can produce OH- ions, making the solution basic. This concept is crucial for determining the acidity of the given salts.
Recommended video:
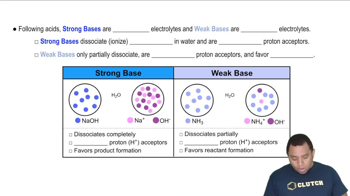
Strong vs. Weak Acids and Bases
Strong acids and bases completely dissociate in water, while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate. For instance, NaOH is a strong base that fully dissociates, leading to a higher pH, whereas NH4Cl is derived from a weak acid (NH4+) and a strong base (Cl-), resulting in a more acidic solution. This distinction is vital for ranking the acidity of the solutions.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance