Each reaction is allowed to come to equilibrium, and then the volume is changed as indicated. Predict the effect (shift right, shift left, or no effect) of the indicated volume change. a. CO(g) + H2O( g) ⇌ CO2(g) + H2(g) (volume is decreased)
This reaction is endothermic. C(s) + CO2(g) ⇌ 2 CO(g) Predict the effect (shift right, shift left, or no effect) of increasing and decreasing the reaction temperature. How does the value of the equilibrium constant depend on temperature?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified Solution
Key Concepts
Le Chatelier's Principle

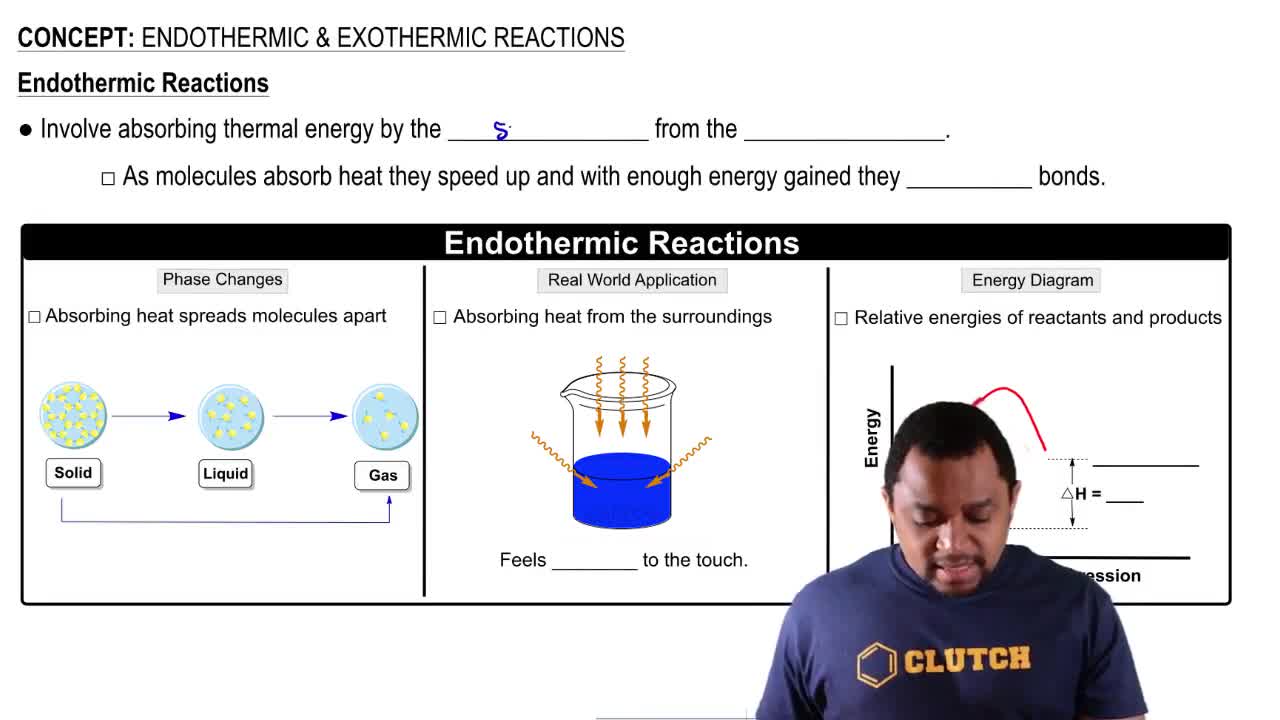
Endothermic Reactions
Equilibrium Constant (K)

Each reaction is allowed to come to equilibrium, and then the volume is changed as indicated. Predict the effect (shift right, shift left, or no effect) of the indicated volume change. b. PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ PCl5(g) (volume is increased)
Each reaction is allowed to come to equilibrium, and then the volume is changed as indicated. Predict the effect (shift right, shift left, or no effect) of the indicated volume change. c. CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(g) (volume is increased)
Coal, which is primarily carbon, can be converted to natural gas, primarily CH4, by the exothermic reaction: C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) Which disturbance will favor CH4 at equilibrium? c. raising the temperature of the reaction mixture
Coal, which is primarily carbon, can be converted to natural gas, primarily CH4, by the exothermic reaction: C(s) + 2 H2(g) ⇌ CH4(g) Which disturbance will favor CH4 at equilibrium? e. adding a catalyst to the reaction mixture
Coal can be used to generate hydrogen gas (a potential fuel) by the endothermic reaction: C(s) + H2O(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2(g) If this reaction mixture is at equilibrium, predict whether each disturbance will result in the formation of additional hydrogen gas, the formation of less hydrogen gas, or have no effect on the quantity of hydrogen gas. e. adding a catalyst to the reaction mixture
