Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Activation Energy
Activation energy is the minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur. It represents the energy barrier that reactants must overcome to form products. In reactions with zero activation energy, the reactants can convert to products without any energy input, suggesting that the reaction can proceed readily under a wide range of conditions.
Recommended video:
Reaction Rate and Temperature
The rate of a chemical reaction is influenced by temperature, as higher temperatures generally increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to more frequent and effective collisions. However, in reactions with zero activation energy, the rate is less sensitive to temperature changes, as the energy barrier for the reaction is nonexistent, allowing the reaction to proceed at a constant rate regardless of temperature fluctuations.
Recommended video:
Kinetics of Gas Phase Reactions
Gas phase reactions involve the interaction of gaseous reactants, and their kinetics can be affected by factors such as pressure, concentration, and temperature. In the case of the given reaction, since it has zero activation energy, the kinetics may not show significant variation with temperature, indicating that the reaction is likely to occur rapidly and consistently in the gas phase.
Recommended video:
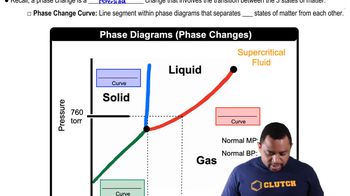
Phase Changes in Diagrams