Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
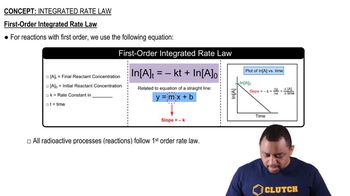
First-Order Reactions
First-order reactions are chemical reactions where the rate is directly proportional to the concentration of one reactant. This means that as the concentration of the reactant decreases, the rate of reaction also decreases. The integrated rate law for a first-order reaction can be expressed as ln([A]₀/[A]) = kt, where [A]₀ is the initial concentration, [A] is the concentration at time t, k is the rate constant, and t is time.
Recommended video:
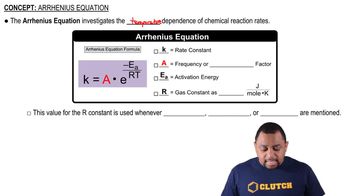
Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation relates the rate constant of a reaction to the temperature and activation energy. It is expressed as k = A * e^(-Ea/RT), where k is the rate constant, A is the frequency factor, Ea is the activation energy, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin. This equation helps in understanding how temperature affects reaction rates and is crucial for calculating k when given Ea and A.
Recommended video:
Fraction Decomposed
The fraction decomposed in a reaction can be calculated using the integrated rate law for first-order kinetics. By rearranging the equation, one can find the concentration of the reactant at a given time and then determine the fraction that has reacted. This is important for understanding the extent of the reaction over a specified time period, such as the 15 minutes mentioned in the question.
Recommended video: