Open Question
A 0.95 m aqueous solution of an ionic compound with the formula MX has a freezing point of -3.0 °C. Calculate the van’t Hoff factor (i) for MX at this concentration.


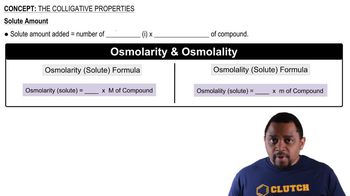

A 0.100 M ionic solution has an osmotic pressure of 8.3 atm at 25 °C. Calculate the van't Hoff factor (i) for this solution.
An aqueous CaCl2 solution has a vapor pressure of 81.6 mmHg at 50 °C. The vapor pressure of pure water at this temperature is 92.6 mmHg. What is the concentration of CaCl2 in mass percent? (Assume complete dissociation of the solute.)
The solubility of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in water at 25 °C is 1.2 g/L. The solubility of chloroform (CHCl3) at the same temperature is 10.1 g/L. Why is chloroform almost ten times more soluble in water than carbon tetrachloride?