Does a photon of red light with a frequency of 4.29⨉1014 Hz have sufficient energy to promote an electron from the valence band to the conduction band in a sample of silicon (the band gap in silicon is 1.11 eV)?
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Material
Chapter 12, Problem 70
Saran, the polymer used to make saran wrap, is an addition polymer formed from two monomers—vinylidene chloride and vinyl chloride. Draw the structure of the polymer. (Hint: The monomers alternate.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the monomers: Vinylidene chloride is \( \text{CH}_2=\text{CCl}_2 \) and vinyl chloride is \( \text{CH}_2=\text{CHCl} \).
Understand that in an addition polymerization, the double bonds in the monomers open up to form single bonds, linking the monomers together.
Recognize that the polymer is formed by alternating the two monomers, so the repeating unit will consist of one vinylidene chloride and one vinyl chloride.
Draw the repeating unit by connecting the carbon atoms of the monomers in a head-to-tail fashion: \( -\text{CH}_2-\text{CCl}_2-\text{CH}_2-\text{CHCl}- \).
Extend the repeating unit to show the polymer chain, indicating that the pattern continues indefinitely: \( -[\text{CH}_2-\text{CCl}_2-\text{CH}_2-\text{CHCl}]_n- \), where \( n \) represents the number of repeating units.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Addition Polymerization
Addition polymerization is a chemical reaction in which monomers with unsaturated bonds (like double bonds) react to form a polymer. This process involves the breaking of the double bonds in the monomers, allowing them to link together in long chains. The resulting polymer retains the main chain of the original monomers, making it a key method for synthesizing various plastics and synthetic materials.
Recommended video:
Guided course
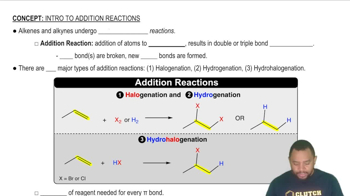
Addition Reactions
Monomer Structure
Monomers are the basic building blocks of polymers, typically small molecules that can join together to form larger structures. In the case of saran wrap, the monomers vinylidene chloride and vinyl chloride each contain a carbon-carbon double bond, which is crucial for the polymerization process. Understanding the structure of these monomers helps in visualizing how they will combine to form the polymer.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Resonance Structures
Polymer Structure and Alternation
The structure of a polymer is determined by the arrangement of its monomers. In the case of saran, the hint indicates that the monomers alternate, meaning that the polymer chain will consist of repeating units of vinylidene chloride and vinyl chloride in an alternating pattern. This alternation can affect the physical properties of the polymer, such as its strength and flexibility.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Resonance Structures
Related Practice
Textbook Question
467
views
Open Question
What is the wavelength of light (in nm) emitted when an electron moves from the conduction band to the valence band in a sample of diamond, which has a band gap of 5.5 eV?
Textbook Question
Teflon is an addition polymer formed from the monomer shown here. Draw the structure of the polymer.
1016
views
Textbook Question
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is an addition polymer with the struc- ture shown here. Draw the structure of the monomer.
1109
views
Textbook Question
Copper iodide crystallizes in the zinc blende structure. The sep- aration between nearest neighbor cations and anions is approximately 311 pm, and the melting point is 606 °C. Potassium chloride, by contrast, crystallizes in the rock salt structure. Even though the separation between nearest-neighbor cations and anions is greater (319 pm), the melting point of potassium chlo- ride is higher (776 °C). Explain.
470
views
Open Question
The volume of a unit cell of diamond is 0.0454 nm³, and the density of diamond is 3.52 g/cm³. Find the number of carbon atoms in a unit cell of diamond.
