Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enthalpy (∆H)
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic quantity that represents the total heat content of a system. It is defined as the internal energy of the system plus the product of its pressure and volume (H = U + PV). In chemical reactions, the change in enthalpy (∆H) indicates whether the reaction is exothermic (releases heat, ∆H < 0) or endothermic (absorbs heat, ∆H > 0).
Recommended video:
Internal Energy (∆E)
Internal energy is the total energy contained within a system, encompassing kinetic and potential energies of the particles. The change in internal energy (∆E) during a reaction can be calculated using the first law of thermodynamics, which states that the change in internal energy is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system (∆E = q - W).
Recommended video:
Relationship between ∆H and ∆E
The relationship between enthalpy change (∆H) and internal energy change (∆E) is given by the equation ∆H = ∆E + P∆V, where P is the pressure and ∆V is the change in volume. For reactions occurring at constant pressure, if the volume change is negligible, ∆H can be approximated as equal to ∆E. However, if there is a significant volume change, this relationship must be considered to accurately calculate ∆E.
Recommended video:
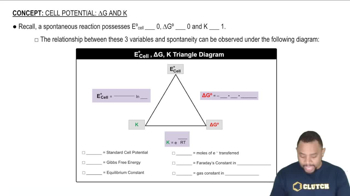
Relationship between ∆E°, ∆G°, and K