Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enthalpy Change (∆H)
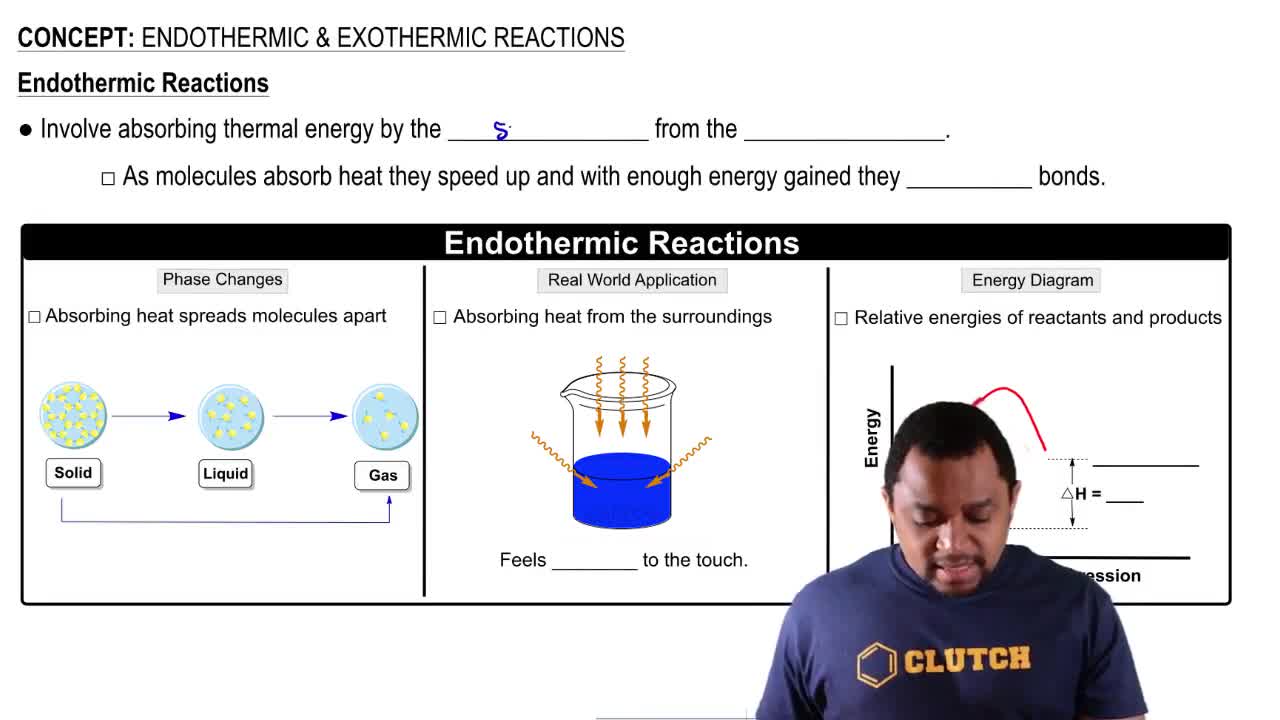
Enthalpy change (∆H) is a measure of the heat content of a system at constant pressure. It indicates whether a reaction absorbs heat (endothermic, ∆H > 0) or releases heat (exothermic, ∆H < 0). In the context of the given reaction, a change in temperature suggests that heat is either absorbed or released, which directly relates to the enthalpy change.
Recommended video:
Exothermic vs. Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions release heat to the surroundings, resulting in an increase in temperature of the surroundings, while endothermic reactions absorb heat, leading to a decrease in temperature of the surroundings. The temperature increase from 320 K to 370 K in the reaction indicates that heat is being absorbed, suggesting that the reaction is endothermic.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Ideal Gas Law and Thermodynamic Principles
The Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT) relates pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas. In this scenario, the constant pressure (1 atm) and the change in temperature imply that the volume may also change, affecting the internal energy and enthalpy of the system. Understanding these principles helps in analyzing how energy is transferred during the reaction.
Recommended video: