Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exothermic Reactions
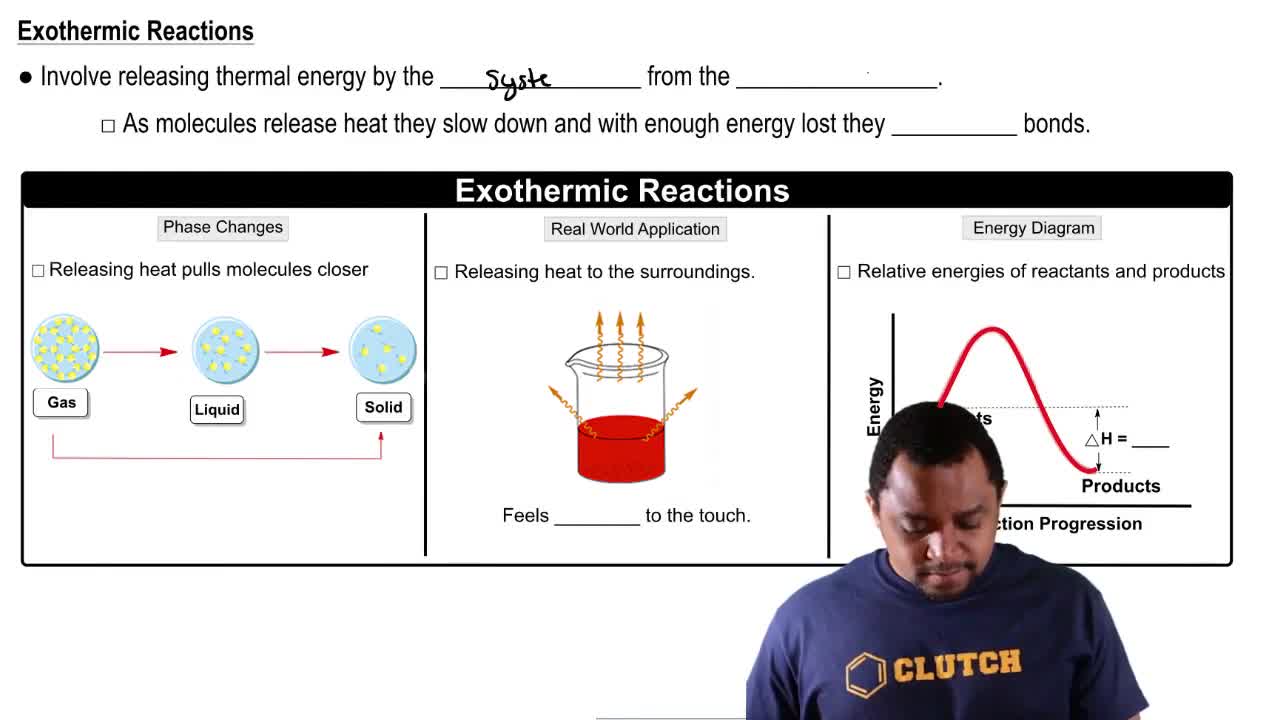
Exothermic reactions are chemical processes that release energy, usually in the form of heat, to the surroundings. This occurs when the total energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants, resulting in a net release of energy. Common examples include combustion reactions, where fuels react with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing significant energy.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Enthalpy Change (ΔH)
Enthalpy change, denoted as ΔH, is a measure of the total heat content of a system. In chemical reactions, a negative ΔH indicates that energy is released (exothermic), while a positive ΔH indicates energy is absorbed (endothermic). Understanding ΔH is crucial for predicting the energy changes associated with different processes and determining which will release the most energy.
Recommended video:
Bond Energy
Bond energy refers to the amount of energy required to break a bond between two atoms. When chemical bonds are formed during a reaction, energy is released, and the total energy released is related to the bond energies of the reactants and products. A process that involves the formation of strong bonds and the breaking of weaker bonds will typically release more energy, making bond energy a key factor in evaluating energy release in reactions.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance