Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation Number
An oxidation number is a theoretical charge assigned to an atom in a compound, reflecting its degree of oxidation or reduction. It helps in understanding electron transfer in redox reactions. The oxidation number can be positive, negative, or zero, depending on the atom's bonding and electron sharing with other atoms.
Recommended video:
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
There are specific rules for assigning oxidation numbers, such as: the oxidation number of an element in its standard state is zero, the oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals its charge, and in compounds, hydrogen typically has an oxidation number of +1 while oxygen usually has -2. These rules guide the determination of oxidation states in complex compounds.
Recommended video:
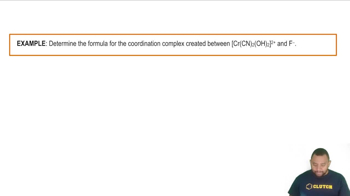
Complex Ions and Coordination Compounds
Complex ions consist of a central metal atom bonded to surrounding ligands, which can be neutral molecules or ions. In coordination compounds like H2PtCl6, the oxidation state of the central metal (platinum) is influenced by the charges of the ligands. Understanding the structure and bonding in these compounds is essential for accurately assigning oxidation numbers.
Recommended video:
Coordination Complexes Example