Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation Numbers
Oxidation numbers are a way to keep track of electron transfer in chemical reactions. They represent the hypothetical charge an atom would have if all bonds were ionic. The rules for assigning oxidation numbers include that the oxidation number of an element in its elemental form is zero, and for monoatomic ions, it equals the charge of the ion.
Recommended video:
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers
There are specific rules for assigning oxidation numbers, such as oxygen typically having an oxidation number of -2, hydrogen being +1 when bonded to non-metals, and the sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound equaling zero. Understanding these rules is essential for accurately determining the oxidation states of elements in a compound.
Recommended video:
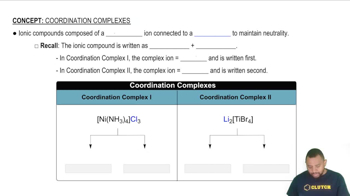
Complex Compounds
Complex compounds, like VOCl3, consist of a central atom bonded to surrounding atoms or groups. In this case, vanadium (V) is the central atom, and its oxidation state must be determined in relation to the oxidation states of chlorine (Cl) and oxygen (O). Recognizing how to analyze the structure of complex compounds is crucial for assigning oxidation numbers correctly.
Recommended video:
Coordination Complexes I and II