Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
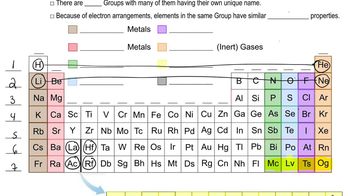
Periodic Table Groups
The periodic table is organized into groups (columns) that share similar chemical properties. For example, Group 1 contains alkali metals, which are highly reactive and typically found in nature as compounds rather than in pure form. Group 17 contains halogens, known for their reactivity and tendency to form salts with metals. Understanding these group characteristics is essential for identifying elements and their behaviors.
Recommended video:
Periodic Table: Group Names
Conductivity of Elements
Elements can be classified based on their ability to conduct electricity. Metals, typically found on the left side of the periodic table, are good conductors, while nonmetals, located on the right, are generally poor conductors. This distinction is crucial for evaluating the properties of elements, especially when determining their classifications as metals, nonmetals, or metalloids.
Recommended video:
Elemental Forms of Elements
Physical States of Elements
Elements can exist in different physical states at room temperature: solid, liquid, or gas. Most metals are solid at room temperature, while nonmetals can be gases (like oxygen) or solids (like sulfur). Understanding the physical state of an element helps in predicting its behavior and interactions, which is vital for answering questions about their properties and classifications.
Recommended video: