Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. In this process, ions are generated, accelerated, and then passed through a magnetic field, where their paths are influenced by their mass and charge. This allows for the identification and quantification of different ions based on their mass.
Recommended video:
Lorentz Force
The Lorentz force is the force experienced by a charged particle moving through a magnetic field. It is perpendicular to both the velocity of the particle and the direction of the magnetic field. The magnitude of the deflection of an ion in a magnetic field is influenced by its mass and charge, with lighter ions experiencing greater deflection than heavier ions.
Recommended video:
Types of Intermolecular Forces
Ion Deflection in Magnetic Fields
In a magnetic field, ions with different masses and charges will follow different trajectories. Lighter ions, having less mass, are deflected more than heavier ions when subjected to the same magnetic field strength. This principle is crucial for separating ions based on their mass-to-charge ratios in mass spectrometry.
Recommended video:
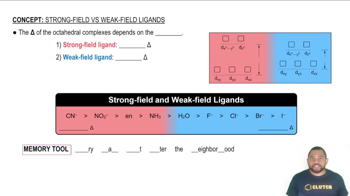
Strong-Field Ligands result in a large Δ and Weak-Field Ligands result in a small Δ.