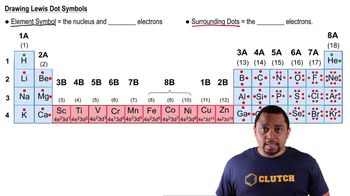
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Atomic Number
The atomic number of an element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of its atoms. It uniquely identifies an element and determines its position in the periodic table. For example, carbon has an atomic number of 6, meaning it has 6 protons.
Recommended video:
Element Symbols
Each chemical element is represented by a unique one- or two-letter symbol, often derived from its English or Latin name. For instance, carbon is represented by 'C' and argon, which has 18 protons, is represented by 'Ar'. These symbols are used universally in chemical equations and formulas.
Recommended video:
Electrons and Neutral Atoms
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons, balancing the overall charge. Therefore, an element with 23 electrons must also have 23 protons, identifying it as vanadium, which has the atomic number 23. This relationship is crucial for understanding atomic structure and chemical behavior.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Neutral Compounds