Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear reactions involve changes in an atom's nucleus and can result in the transformation of one element into another. These reactions include processes such as alpha decay, beta decay, and electron capture. Understanding the type of nuclear reaction is essential for writing balanced nuclear equations, as it dictates the particles involved and the resulting isotopes.
Recommended video:
Electron Capture
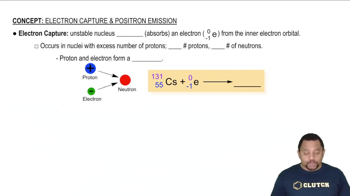
Electron capture is a type of radioactive decay in which an electron from the innermost energy level is captured by the nucleus, combining with a proton to form a neutron. This process decreases the atomic number of the element by one while keeping the mass number the same. Recognizing this mechanism is crucial for accurately representing the changes in the nuclear equation.
Recommended video:
Balancing Nuclear Equations
Balancing nuclear equations requires ensuring that the total number of protons and neutrons is the same on both sides of the equation. This involves accounting for the particles emitted or absorbed during the reaction, such as electrons, positrons, or neutrinos. Mastery of this concept is vital for correctly formulating the nuclear equation for processes like electron capture.
Recommended video:
Balancing Chemical Equations
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance