Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
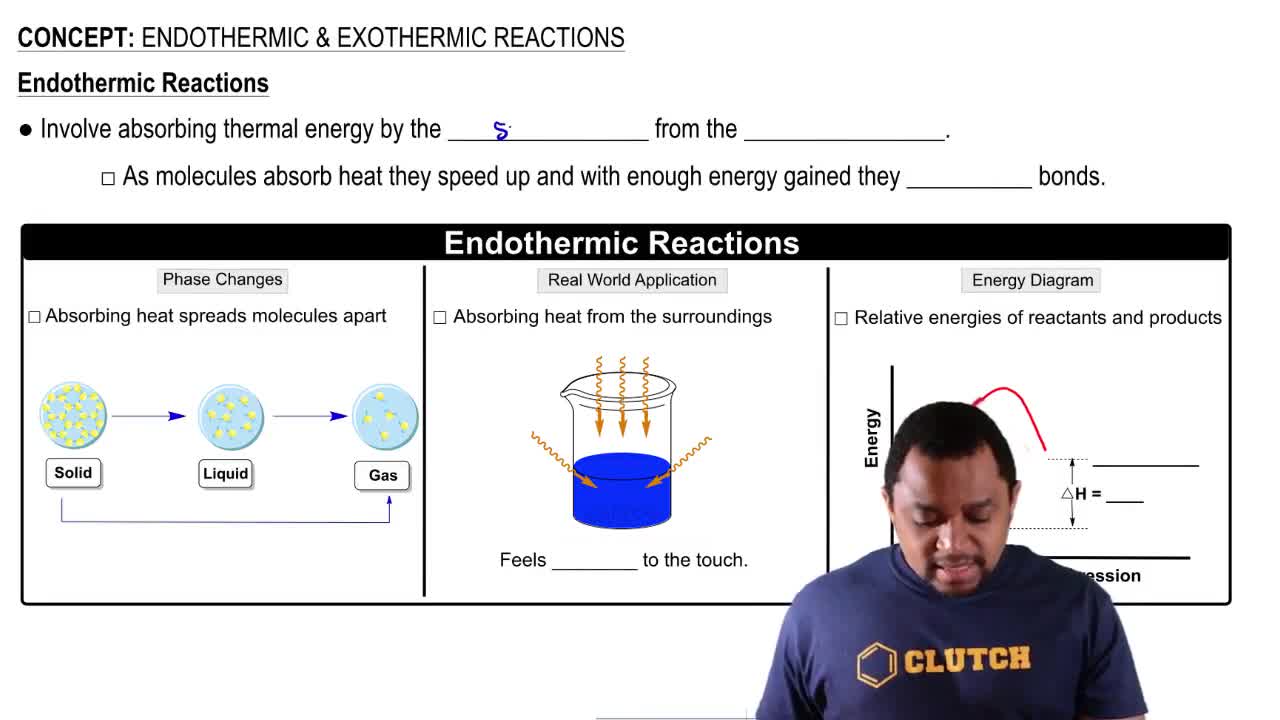
Endothermic Reactions
Endothermic reactions are chemical processes that absorb heat from their surroundings, resulting in a decrease in temperature of the environment. In these reactions, the enthalpy change (ΔH) is positive, indicating that energy is required for the reaction to proceed. Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing the spontaneity of reactions, as it influences how temperature affects the reaction's favorability.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Spontaneity of Reactions
The spontaneity of a reaction refers to its ability to occur without external intervention. It is determined by the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG), where a negative ΔG indicates a spontaneous process. For endothermic reactions, temperature plays a significant role; at higher temperatures, the entropy change (ΔS) can outweigh the positive enthalpy change, potentially making the reaction spontaneous.
Recommended video:
Temperature and Entropy
Temperature and entropy are key factors in determining the spontaneity of a reaction. Entropy (ΔS) measures the disorder or randomness of a system, and an increase in entropy generally favors spontaneity. In endothermic reactions, as temperature increases, the contribution of the TΔS term in the Gibbs free energy equation (ΔG = ΔH - TΔS) can lead to a negative ΔG, thus promoting spontaneity at elevated temperatures.
Recommended video:
Entropy and Physical Changes