Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Arrhenius Equation
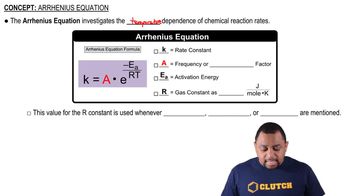
The Arrhenius equation describes how the rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction depends on temperature (T) and activation energy (Ea). It states that k = Ae^(-Ea/RT), where A is the pre-exponential factor. As temperature increases, the exponential term becomes larger, leading to an increase in k, which generally accelerates the reaction rate.
Recommended video:
Equilibrium Constant (Kc)
The equilibrium constant (Kc) quantifies the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants at equilibrium for a reversible reaction. For a reaction with forward rate constant (kf) and reverse rate constant (kr), Kc = kf/kr. Changes in temperature can affect kf and kr differently, influencing the value of Kc.
Recommended video:
Equilibrium Constant Expressions
Le Chatelier's Principle
Le Chatelier's Principle states that if a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in temperature, pressure, or concentration, the system will adjust to counteract that change and restore a new equilibrium. For exothermic reactions, increasing temperature shifts the equilibrium position towards the reactants, resulting in a decrease in Kc.
Recommended video: