Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Covalent Network Solids
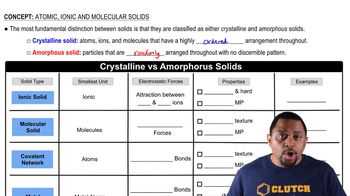
Covalent network solids, like silicon nitride, consist of a continuous network of covalent bonds, creating a rigid structure. This extensive bonding leads to high melting points and hardness but also results in brittleness, as the strong bonds do not allow for easy deformation. When stress is applied, these materials tend to fracture rather than bend.
Recommended video:
Crystalline vs Amorphous Solids
Metallic Bonding
In metals like copper, atoms are held together by metallic bonds, which involve a 'sea of electrons' that are free to move. This electron mobility allows metals to deform plastically under stress, making them malleable and ductile. The ability to absorb energy through deformation contributes to the toughness of metals compared to covalent network solids.
Recommended video:
Brittleness vs. Ductility
Brittleness refers to a material's tendency to break or shatter under stress without significant deformation, while ductility is the ability to stretch or deform without breaking. Silicon nitride's strong covalent bonds contribute to its brittleness, as it cannot undergo plastic deformation like ductile metals, which can absorb and redistribute stress through movement of dislocations.
Recommended video:
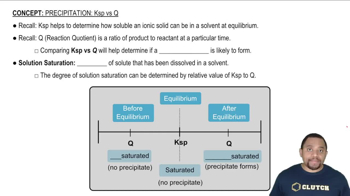
Ksp vs Q in Precipitation