Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Crystalline Solids
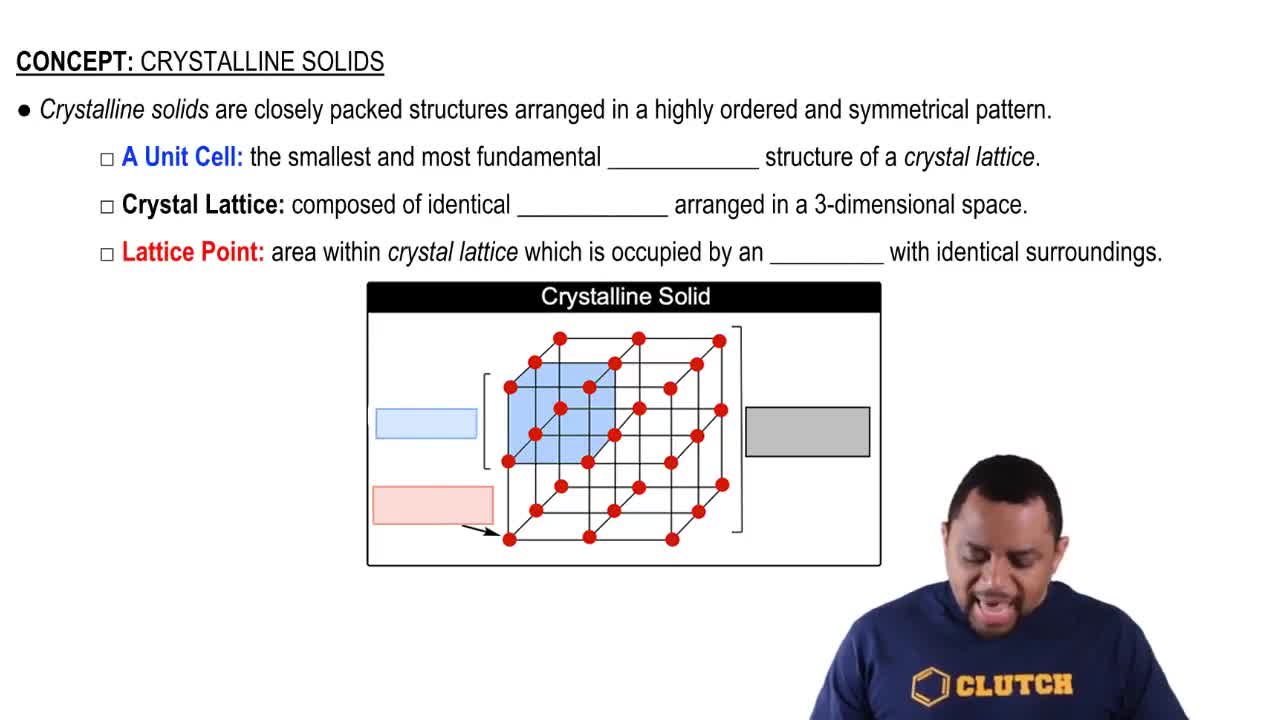
Crystalline solids are materials whose constituents, such as atoms, ions, or molecules, are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. This regular arrangement leads to distinct geometric shapes and specific physical properties, such as melting points and solubility. Understanding the nature of crystalline solids is essential for classifying them into different types based on their bonding and structure.
Recommended video:
Crystalline Solids Structure
Types of Crystalline Solids
Crystalline solids can be classified into four main types: ionic, covalent (or network), metallic, and molecular solids. Each type is characterized by the nature of the bonding between its particles. For example, ionic solids consist of ions held together by electrostatic forces, while metallic solids feature a 'sea of electrons' that allows for conductivity and malleability. Recognizing these categories helps in understanding their properties and behaviors.
Recommended video:
Crystalline Solids Structure
Examples of Crystalline Solids
Providing specific examples of each class of crystalline solids aids in illustrating their unique characteristics. For instance, sodium chloride (table salt) is an ionic solid, diamond represents a covalent solid, copper is a metallic solid, and ice is a molecular solid. These examples highlight the diversity in structure and properties among different types of crystalline solids, reinforcing the classification system.
Recommended video:
Crystalline Solids Example