Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
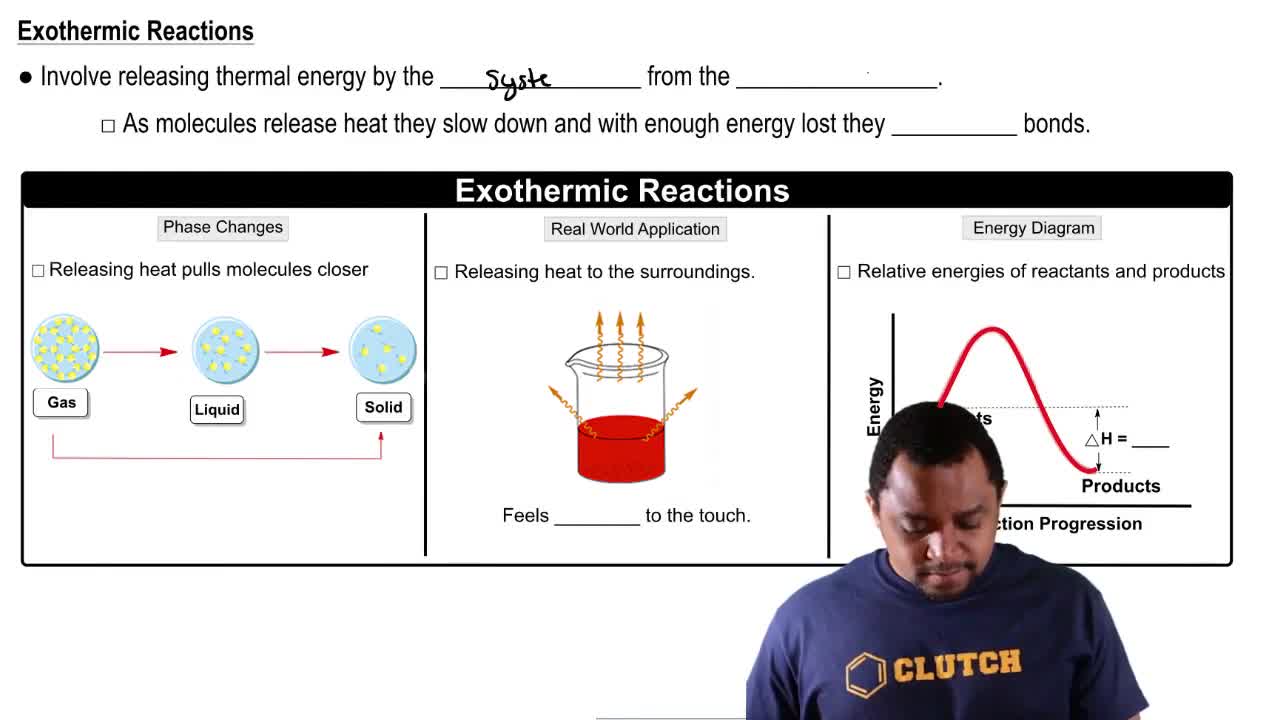
Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are chemical processes that release energy, usually in the form of heat, to the surroundings. This release of energy often results in an increase in temperature of the surrounding environment. Understanding whether a reaction is exothermic helps predict its behavior under different temperature conditions, particularly in relation to spontaneity.
Recommended video:
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Spontaneity of Reactions
A reaction is considered spontaneous if it occurs without the need for continuous external energy input. The spontaneity of a reaction is determined by the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG); if ΔG is negative, the reaction is spontaneous. Factors such as enthalpy, entropy, and temperature play crucial roles in determining whether a reaction will be spontaneous under specific conditions.
Recommended video:
Temperature's Effect on Spontaneity
Temperature significantly influences the spontaneity of reactions, particularly those involving changes in entropy. For exothermic reactions, lower temperatures generally favor spontaneity due to the negative ΔH (enthalpy change). However, at higher temperatures, the entropy change (ΔS) can also affect spontaneity, making it essential to consider both enthalpy and entropy when evaluating reaction behavior across different temperature ranges.
Recommended video:
Spontaneity and Temperature
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance