Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Dot Structures
Lewis dot structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. They use dots to represent valence electrons and lines to represent covalent bonds. Understanding how to draw these structures is essential for visualizing molecular geometry and predicting reactivity.
Recommended video:
Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
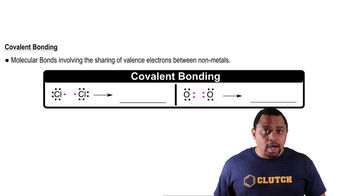
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding occurs when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, allowing them to achieve a full outer electron shell. In organic compounds like naphthalene, carbon atoms typically form four covalent bonds, leading to complex structures. Recognizing how to identify and represent these bonds is crucial for constructing accurate molecular representations.
Recommended video:
Resonance Structures
Resonance structures are different ways of drawing the same molecule that illustrate the delocalization of electrons. In naphthalene, the double bonds can be arranged in multiple configurations, which helps explain its stability and reactivity. Understanding resonance is important for predicting the behavior of aromatic compounds in chemical reactions.
Recommended video: