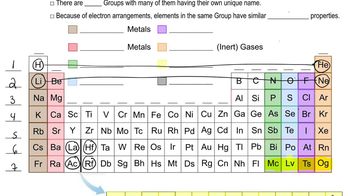
Textbook Question
Take a guess. What do you think is a likely ground-state electron configuration for the sodium ion, Na+, formed by loss of an electron from a neutral sodium atom?
601
views
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory
Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory Problem 123
Problem 123 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance