Textbook Question
Each of the following pairs of elements will react to form a binary ionic compound. Write the formula of each compound formed, and give its name. (d) Barium and flourine
435
views
 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory
Ch.6 - Ionic Compounds: Periodic Trends and Bonding Theory Problem 78c
Problem 78c Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

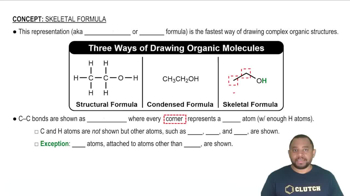

Each of the following pairs of elements will react to form a binary ionic compound. Write the formula of each compound formed, and give its name. (d) Barium and flourine
Element X reacts with element Y to give a product containing X3+ ions and Y2-ions. (a) Is element X likely to be a metal or a nonmetal? Explain.
Element X reacts with element Y to give a product containing X3+ ions and Y2-ions. (b) Is element Y likely to be a metal or a nonmetal? Explain.
Element X reacts with element Y to give a product containing X3+ ions and Y2-ions. (d) In what groups of the periodic table are elements X and Y likely to be found?